Sustainable Food Systems
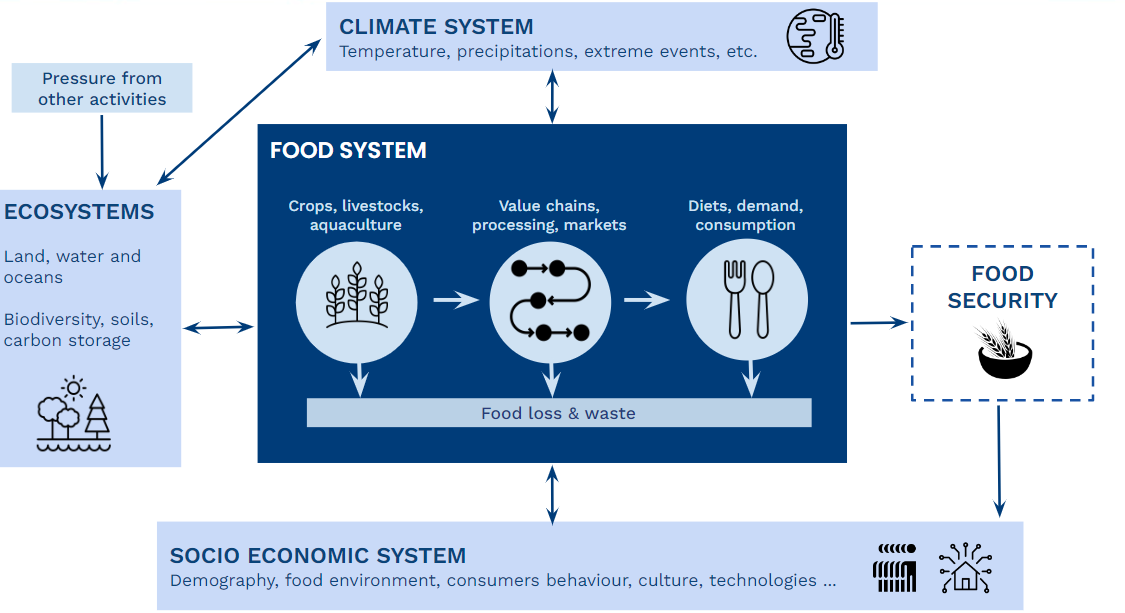
Food system is both a challenge and a central lever when it comes to sustainability: food systems are pivotal to climate change, ecosystem protection, social equity and food security. Sustainability in food production and consumption has emerged as a main concern, driving innovation, and redefining industry practices, including for risk management.
Since the 1980’s, the world temperature has been on a rising slope due to human activity emissions. The temperature increase threatens food security and access to clean water. Climate change has the potential to drive the emergence of new hazards, increases the exposure to known hazards and changes the levels of nutrients in the agricultural soil and ultimately in food (U.S. Global Change Research Program, 2016 [1]).
Food systems are also heavily impacted by changes in other systems (IPCC, 2020 [3]): extreme weather events are disturbing the agri-food production globally, rising demography and changes in consumer behavior are impacting the balance between demand and offer on many foodstuffs, soils degradation and loss in biodiversity are diminishing productivity and resilience of crops.
International commitments to limit global warming such as the COP28 in 2023 are driving actions to mitigate (net-zero emissions for 2030), adapt (deal with current climate impacts), finance (enabling countries to manage their climate goals) and collaborate in the hope of a more livable planet.
If climate change impacts food production, the opposite is also true: food production causes more than one third of the global GHG emissions (FAO, 2021 [2]), which have a direct impact on global warming. These GHG are emitted for the most part at the farming stage (fertilization, manure, soil work, etc.), but also during food manufacturing, storage and transport. Food systems also take part in biodiversity degradation, soil depletion and erosion.
references
[1] U.S. Global Change Research Program, 2016. The Impact of Climate Change on Human Health in the United States: a scientific assessment. [Crimmins, A. et al]
[2] FAO, 2021: Food systems account for more than one third of global greenhouse emissions.
[3] IPCC, 2019. Climate Change and Land: an IPCC special report on climate change, desertification, land degradation, sustainable land management, food security, and greenhouse gas fluxes in terrestrial ecosystems [P.R. Shukla et al.]