definition
The term “dioxins” refers to two categories of differently chlorinated compounds consisting of 75 polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins (PCDD) and 135 polychlorinated dibenzofurans (PCDF). Dioxins (PCDD/F) have similar chemical and physical properties. The 17 compounds chlorinated in 2,3,7,8 positions are particularly toxic and simultaneously persistent. They accumulate in the fatty tissue of animals and humans.
Under standard atmospheric conditions, dioxins are chemically and thermally stable, soluble in organic solvents and fats, and almost insoluble in water.
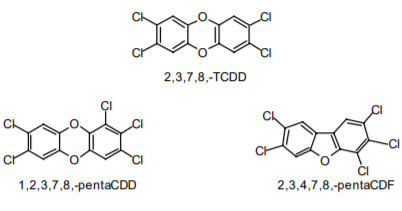
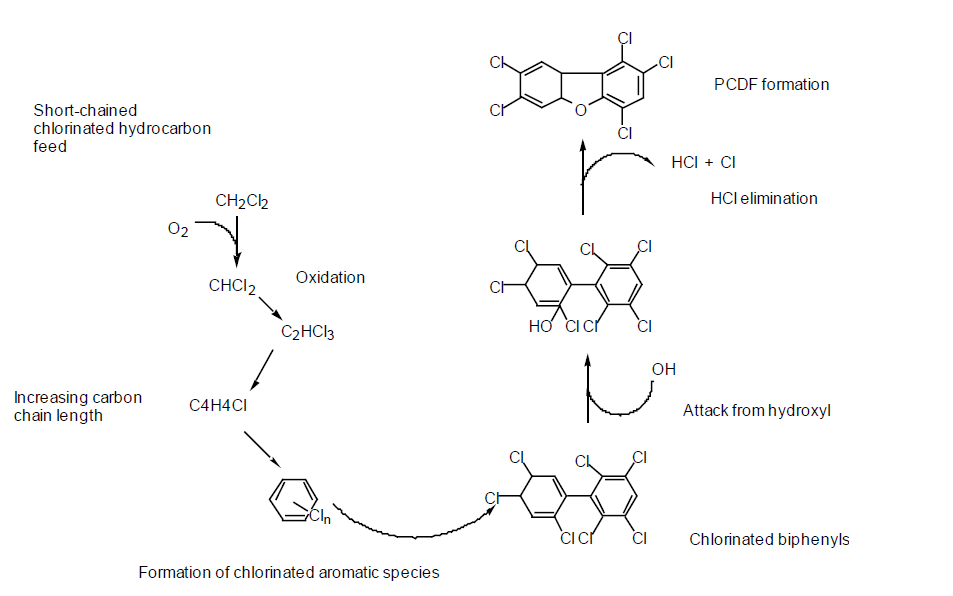
Dioxins are neither manufactured nor used industrially but result as by-products during combustion processes, in particular when organic carbon compounds are burned in the presence of chlorine and temperatures of at least 300 degrees occur, and chemical processes, in particular manufacture of chlorinated chemicals.
GOING FURTHER
Discover what Mérieux NutriSciences can do about this topic on our website: SERVICE PAGEBLOG ARTICLE You can also get more precise data using our specialized digital tools…