definition
Chlorates and Perchlorates were used in the past for different uses, including as pesticides. However, now food contamination seems to come mainly from water disinfection products or by-products.
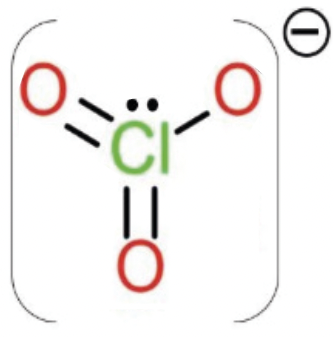
Chlorates (ClO3)– are salts of chloric acid; sodium and potassium chlorates were used in the past as herbicides, but are currently no longer authorized in Europe for plant protection products. Chlorates can mainly contaminate food due to the industrial use of chlorinated (rinsing) water, chlorine-based disinfectants and additives and processing aids with chlorate residues.
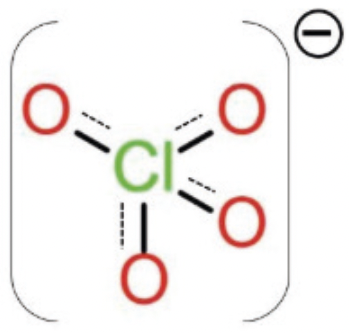
Perchlorates (ClO4)– are salts of perchloric acid, naturally present in the environment in mineral deposits or in the soil and groundwater as a result of perchlorates formed in the atmosphere. It is also due to the use of nitrogen fertilizers and ammonium perchlorates in various products and industrial processes, as well as a result of water disinfection with sodium hypochlorite. Perchlorates are also used as industrial chemicals and pharmaceuticals, especially as rocket propellants and in fireworks. Water, soil and fertilizers are considered to be potential sources of perchlorate contamination in food.