definition
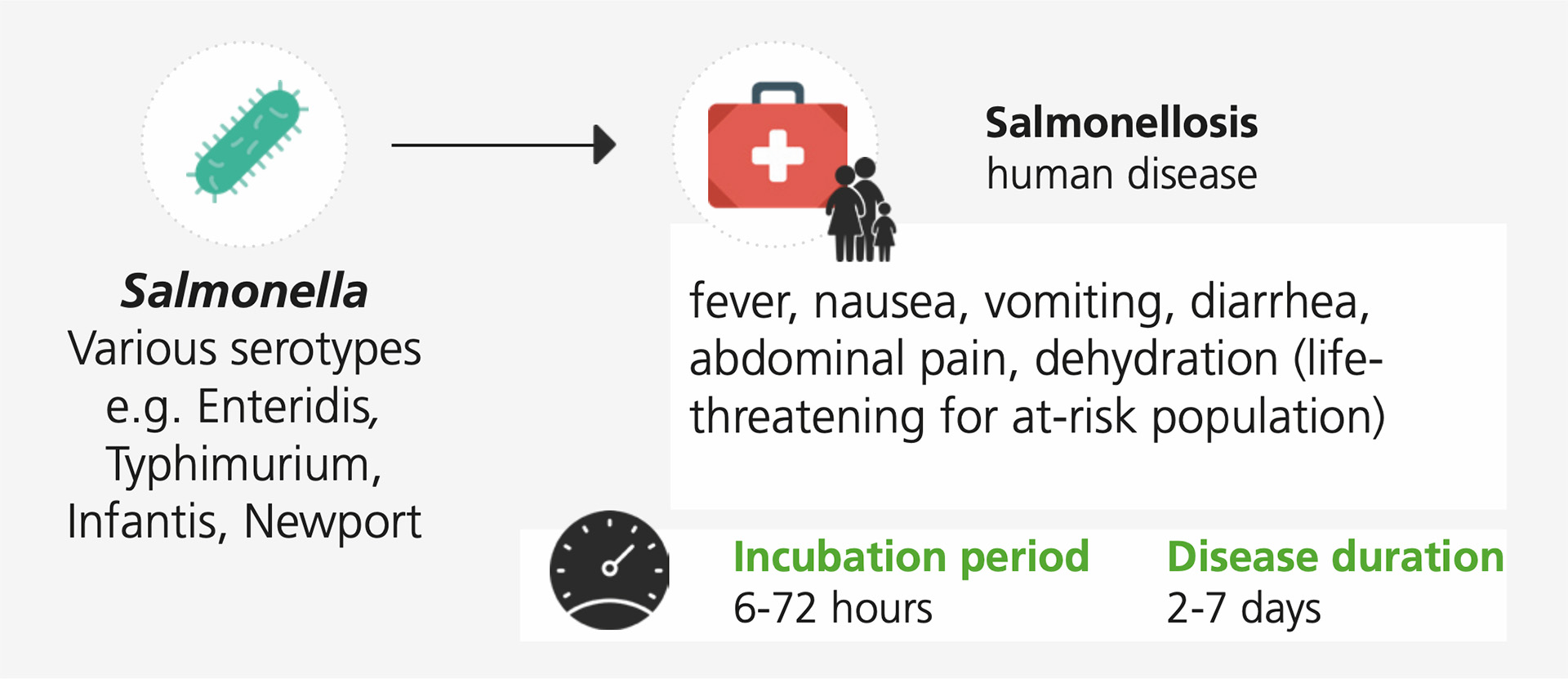
Organisms of the Salmonella genus, named after Daniel Elmer Salmon (1850–1914), an American veterinary surgeon, are Gram-negative non-spore forming rod-shaped bacilli, mostly motile and facultatively anaerobes, of the family Enterobacteriaceae. The two known species of Salmonella are Salmonella bongori and Salmonella enterica, the latter is the type species further divided into six subspecies that include over 2,600 serotypes. They are intracellular pathogens, responsible of an enteric or systemic sometimes fatal disease. Salmonellae are clinically classified as typhoidal (agents of typhoid and paratyphoid fever, directly transmitted among humans, e.g. Salmonella Typhi, Salmonella Paratyphi) and non-typhoidal (common agents of food-borne salmonellosis and zoonotic diseases, e.g. Salmonella Enteritidis, Salmonella Typhimurium).